Trance Music Production: How to Make Hypnotic Electronic Dance Music
With old-school electronic music like house and techno returning to mainstream prominence, it’s no surprise that many producers are revisiting niche 90s subgenres like trance. You may even be wondering how trance music production works.
The good news is that with a bit of creativity and know-how, it’s not as complicated as you may think to start producing trance music.
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know to create entrancing electronic dance music that will captivate your audience.
By the end, you’ll have all the music theory tips, gear recommendations and production techniques to get started.
What is Trance Music?
Trance music is a subgenre of electronic dance music (EDM) characterized by repetitive, fast-paced beats, melodic phrases, and a mesmerizing, hypnotic quality.
Originating in the early 1990s, trance has roots in the European club scene and has since evolved into various subgenres like progressive house, Eurodance, and psytrance.
Some well-known trance artists include Armin van Buuren, Paul van Dyk, and Tiësto.
Trance music continues to be a staple in the EDM community, offering a unique blend of rhythm and melody that transports listeners to a state of euphoria.
Trance Music Production Theory Tips
When producing trance music, it’s essential to have a basic grasp of a handful of essential music theory concepts.
Let’s take a look at a few key theory components to keep in mind when writing trance music.
Trance Rhythms
Trance music typically has a tempo ranging from 130 to 160 BPM, with the kick drum providing a steady, driving rhythm in a four-on-the-floor 4/4 pattern.
Trance often incorporates additional percussion elements, such as claps or snares on beats 2 and 4, and hi-hats on offbeats or 16th notes, to add complexity and energy to the beat.
So, experiment with varying drum patterns, syncopation, and polyrhythms to keep the rhythm section engaging and dynamic.
Common Trance Melodies
Trance melodies are typically simple, memorable, and emotional, serving as the core of the track.
To create an uplifting, anthemic sound, experiment with different scales and modes, such as the major scale, minor scale or the Lydian mode.
Arpeggios and ostinatos around a certain scale can add movement and energy to the melody and are easily programmed using synth sequencers.
When crafting your melody, consider using repetition and slight variations to create a sense of evolving familiarity and catchiness.
Or consider using call and response patterns, to create a sense of movement and conversation between two opposing motifs.
Trance Chord Progressions
Trance tracks often employ chord progressions that evoke a sense of tension and release, creating an emotional journey for the listener.
Common progressions used in trance music include the I-V-vi-IV and the ii-V-I progressions.
Extended chords are also useful for adding flavor and interest to any chord progression you use.
7th and 9th chords, for example, can add a level of depth and complexity to your harmonies.
Suspended chords and modulations to different keys are known for contributing to a feeling of tension and resolution.
Don’t be afraid to experiment with less conventional chord progressions to set your track apart and create your own unique sound.
Trance Song Structure
Trance music often follows an ABAB structure, alternating between a breakdown section (A) and a climax or “drop” section (B).
This structure helps create dynamic shifts and keeps the listener engaged.
Breakdown sections typically strip away most of the drums, focusing on the melody, and allowing the atmosphere of any pads and chordal harmonies to shine through.
While a build-up gradually reintroduces the rhythmic elements and increases tension.
The climax, or drop, brings all elements together at their most intense, providing a sense of release and euphoria.
Within this basic structure, you can experiment with additional sections and variations, such as intros, outros, and interludes.
The key to a successful trance song structure is to balance tension and release, ensuring the listener remains captivated throughout the track.
Anthony takes us through the basics of song structure.
How to Produce Trance Music
Producing trance music involves several steps, each focusing on different aspects of the track. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you craft an unforgettable trance masterpiece:
1. Develop a concept
Before diving into production, establish the mood, emotion, or theme you want to convey with your track.
The best way to get inspired, especially if you’re just getting started is to listen to your favorite trance artists and take notes on what they’re doing that you liked.
Listen actively—pay attention to the song’s various layers: the rhythms, chords and melodies they used, the sound design tools employed throughout and how the track is arranged.

Johnny shares his process for finding a concept and getting over writer's block.
2. Lay down a rhythmic foundation
Usually, it’s best to start by creating a drum pattern, typically with a 4/4 kick drum, snare or clap on beats 2 and 4, and hi-hats on offbeats. This will give you a rhythmic canvas to start coloring in.
Add additional percussion elements, such as rides or shakers, to create more rhythmic complexity.
Once your drums are started, write a bassline that complements your kick drum and adds energy to your track.
A common approach in trance is to use a rolling or “offbeat” bass pattern, where the bass notes hit between the kick drum hits.
3. Add harmony and create an atmosphere
Start by developing a chord progression that evokes the feeling you’re going for and could support a lead melody—if you’re starting to hear possible melodies as your write your chords, that’s a great sign.
Think about the tone and sound design of your chords too—do you want a stabby, staccato chord sound from a punchy arpeggiated synth?
Or are you looking for lush, atmospheric pads to fill out sonic space and create a sense of depth?
Experiment with layering different synth sounds and using automation or various synth parameters such as filters and ADSR envelopes to create movement and tension.
4. Create a lead melody
Composing a catchy, emotive melody to be the central focus of your track takes time and practice.
There’s no exact science for writing an iconic melody but, knowing your scales, learning to identify intervals and listening to other producers is a tried and true method of strengthening melody writing.
From a sound design perspective, layer multiple synths to create a rich, full-spectrum lead, and use techniques like pitch bending, vibrato, and legato to add expressiveness to your melody lines.
5. Arrange and structure
Arrangement is where your beat, melodies and chords turn into a song.
This decision-making process can be challenging because you need to be confident about the specific adjustments you’ll make to your track to bring it to a finished state.
Subtractive arrangement is a fairly common practice in electronic music production—producers will build up a loop with all the elements they want to incorporate into their track.
Then they’ll take the loop and start subtracting parts from it for each section of the song, often arranging to a vocal melody or a pre-determined song structure.
Many trance tracks are structured using an intro, breakdown, build-up, climax, and outro.
Of course, it’s not uncommon for your arrangement to evolve as you write in new melodies, chords, synths and vocals into your track.
6. Mix and master your track
Mixing and mastering is the final step in music production. It takes time and skill to master both and you’ll need technical expertise, software, plugins and hardware to do a good job.
Mixing is the process of balancing levels, EQing various frequency bands, applying compression, and other mix techniques to create a clean and clear sound.
Mastering is the process of optimizing the overall loudness, clarity, and dynamics using mastering tools like EQ, compression, and limiting.
We’ve written about both mixing and mastering in past articles, if you would like to dive into either topic in-depth.
What Gear Do You Need for Trance Music Production?
To get started with trance music production, you’ll some specific gear and software.
Here’s a few basic tools you’ll need to get started.
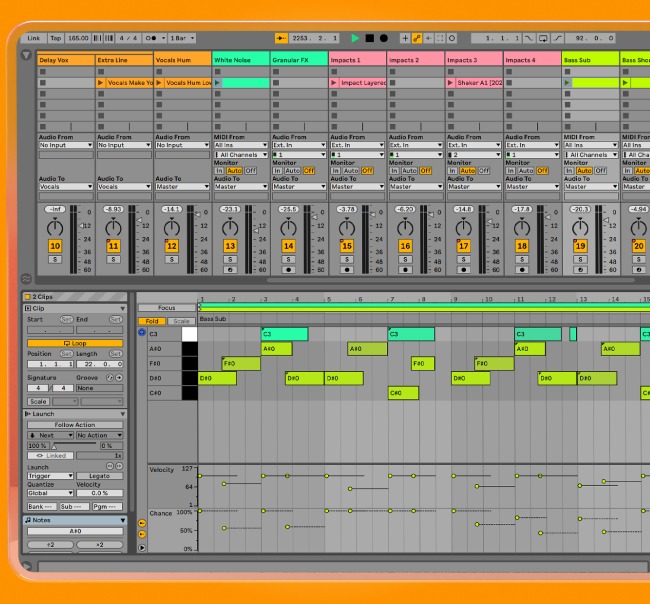
Digital Audio Workstation (DAW)
DAWs are the central point for most music producers, most DAW software contains everything you need to record and produce electronic music.
Popular DAWs for trance music production include Ableton Live, FL Studio, and Logic Pro.
Synthesizers
Trance music production relies heavily on synths to create its characteristic sounds.
Software synths like Serum, Analog Lab Lite, and Usynth Core are popular choices for creating powerful leads, basslines, and pads.
🧠 Hot tip
Samples and loops
High-quality drum, vocal and synth samples are crucial for creating a solid foundation for your track.
It’s best to sign-up for a royalty-free sample marketplace and search for sample packs specifically designed for trance music or EDM in general.
MIDI controller
A MIDI controller, such as a keyboard or pad controller, is key to help you play and record your synth parts more expressively.
You need one if you want to play software synth instruments on your computer.
We’ve explored our favorite MIDI controllers in past articles, if you’re looking to get one for your studio.
Audio interface and monitors
An audio interface is necessary to record any analog gear like synths, mics and guitars into your computer.
Studio monitors provide accurate audio playback, ensuring your mix translates well to different playback systems.
Effects plugins
Aside from software synths and sampler plugins, you’ll need effects plugins to enhance your synths and drums, polish vocals and add stylistic flare.
Many DAWs come with built-in effects, but third-party plugins can offer more advanced features and help you craft a more unique sound.
So take a look around to see what plugins are best for mixing and producing the right sound for your track.
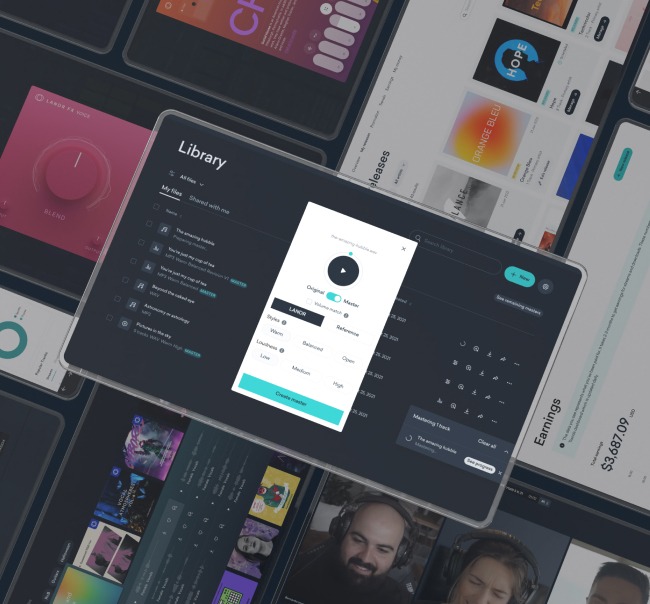
Mastering tools
Mastering is difficult, it take a lot knowledge and practice to truly produce strong masters.
That’s why it’s best for beginners to use AI-based mastering tools to finish their tracks.
LANDR Mastering is an excellent option for generating convincing, loud, radio-ready tracks.
Trance training complete
By incorporating these trance music production tips and techniques into your workflow, you’ll be well on your way to creating hypnotic, captivating tracks that transport listeners to a state of bliss.
Don’t be afraid to experiment and push the boundaries of your creativity.
With the right tools, knowledge, and passion, the sky’s the limit for your trance music production journey.
Gear guides, tips, tutorials, inspiration and more—delivered weekly.
Keep up with the LANDR Blog.