What is Rhythm: How Time, Beat and Meter Work in Music
Rhythm is one of the fundamental aspects of music theory.
Rhythm is one of the fundamental aspects of music theory.
To create great harmonies and melodies you need to understand how rhythm works and how it is used in your tracks.
Rhythm can get complicated very quickly, but if you learn a few simple concepts it’s not as hard to understand as you may think.
In this guide, we’ll unpack everything you need to start applying rhythmic or polyrhythmic concepts in your creative process.
You’ll know how rhythms are subdivided in music, how time signatures work, and how to begin understanding compound and odd time.
What is Rhythm?
Rhythm is the way that music is systematically divided into beats that repeat a specific number of times within a bar at a collectively understood speed or tempo. The rhythm in music, by definition, is the timing and pattern of a collection of sounds.
Rhythm is how musicians connect and play with one another.
At least, that’s the definition you would get if you asked a metronome.
Rhythm is pretty hard to define. It’s what makes music, music.
Notes, melody, and chords can be easily described as vibrations in the airwaves that our eardrums can detect.
Rhythm has more to do with your uniquely human perception of time.
If you asked someone in a drum circle they would probably tell you rhythm is about playing together.
Ask a funk band and they’ll tell you rhythm is about finding a groove.
Neither of those answers are wrong because rhythm is how musicians connect and play with one another. This is the best way to describe rhythm in music. In music, rhythm’s meaning depends on the perspective of the artist.
Rhythm theory: understanding what’s on the page
For our purposes we’ll look at the western way of understanding rhythm.
To understand rhythm are seven basic concepts or elements of rhythm to know:
- Beats and notes
- Measures and time signatures
- Strong and Weak Beats
- Meter
- Syncopation
- Accents
- Tempo
When you master these four concepts you’ll be able to practice better and you’ll get better at using interesting rhythms in your tracks.
1. Beats and notes
There’s a lot to go through when it comes to understanding how to read musical rhythms.
While there might be some confusion about rhythm vs beat. Rhythm is the pattern of sounds, and the beat in rhythm, by definition, is the steady underlying pulse in a rhythm.
But at the core of feeling any rhythm, you have to understand that a musical note represents the duration of time that an instrument will be played.
A musical note represents the duration of time that an instrument will be played.
A whole note represents the longest playing duration but whole notes can be broken down into halves, quarters, eighths and sixteenths.
A half note will occupy half the duration of a whole note, a quarter note will occupy a quarter of the duration of a whole note and so forth.
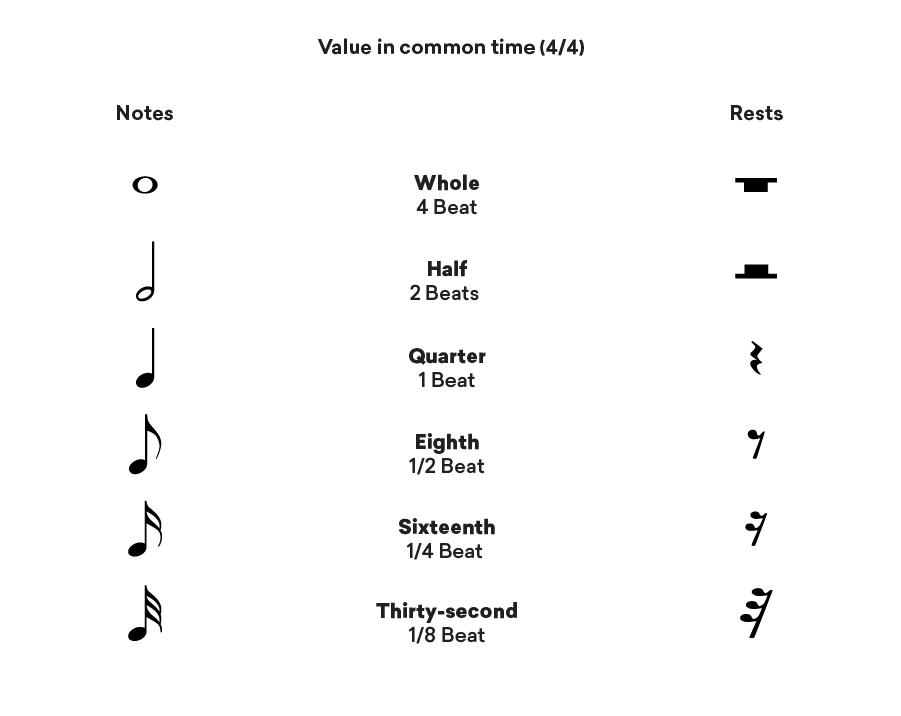
There are many ways that these notes can be changed and organized to represent different rhythms.
But as a foundation for how rhythm is visually and conceptually understood in music your first step is to know how notes are broken down.
2. Time signatures and bars
There is an underlying pulse in all music that can be contained within a specific measure of time.
This measure of time is referred to as a musical bar or measure.
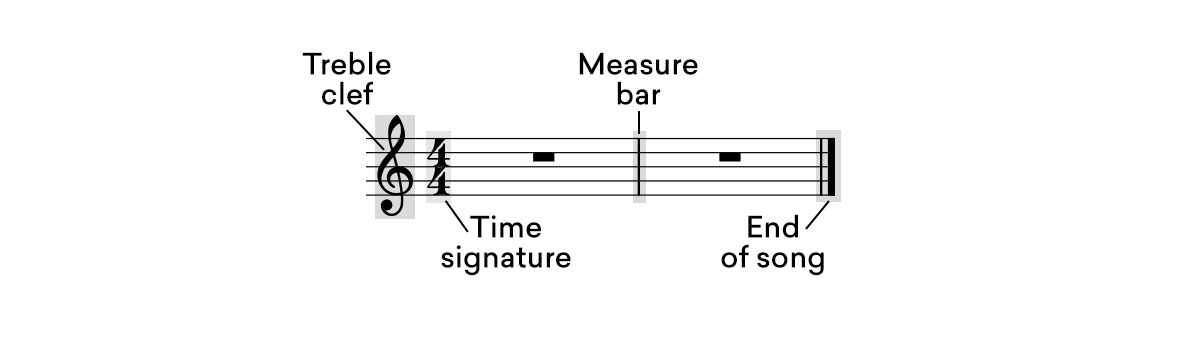
In western music, the time signature of a song dictates how its pulse is measured in each bar and tempo defines how fast the pulse is. This will tell you the beats per measure.
The pulse is represented by a fraction-like symbol that dictates the number of notes per bar and how each note is counted in terms of halves, quarters or sixteenths.
Consider the most common time signature in music– 4/4.
The number four on top says that there are four pulses to one bar, and the number four on the bottom says that these pulses are measured in terms of quarter notes.
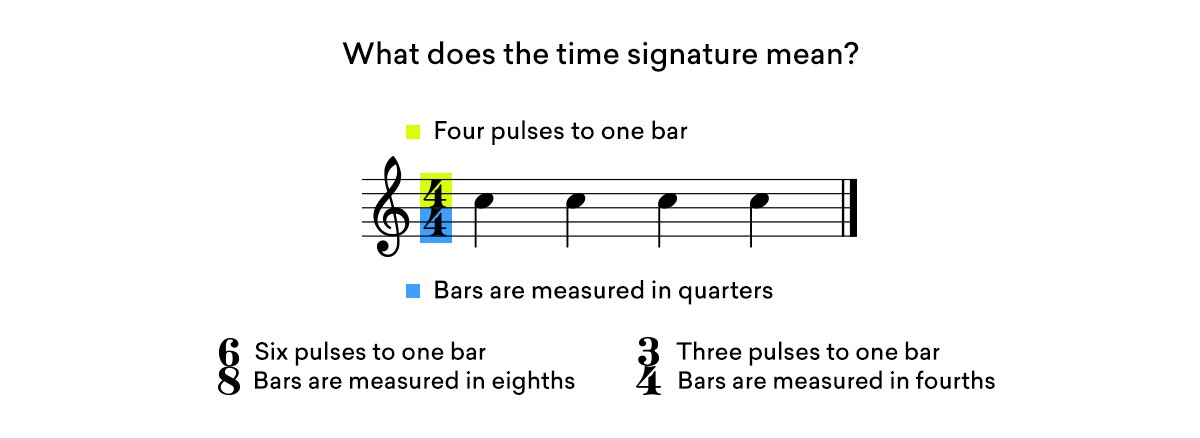
Of course, there are many time signatures in music beyond 4/4.
Every waltz you’ve ever heard is in 3/4 and then there’s the world of compound and odd time.
3. Strong and weak beats
Alright, now that you know how time signatures work and how beats fit into a bar, let’s look at how rhythm works within a bar.
Within a bar there are strong beats that drive the pulse and there are weak beats that counteract the pulse.
Within a bar there are strong beats that drive the pulse and there are weak beats that counteract the pulse.
This push and pull is what adds definition to a measure and makes rhythms easier to hear.
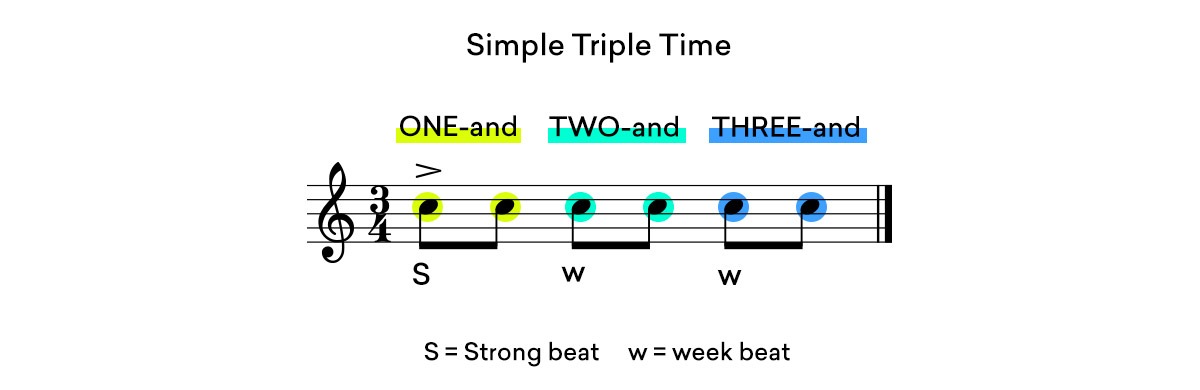
If we consider the common 4/4 measure, the strong beats fall on the first and third quarter notes in the bar and the weak beats fall on the second and fourth quarter notes.

In a 3/4 measure, the strong beat falls on the first quarter note and the weak beats fall on the second and third.

When you know how strong and weak beats sound in a musical measure you can hear them everywhere.
The pushing ONE-two, ONE-two pulse of a kick drum on a 4/4 disco track or the lilting ONE-two-three, ONE-two-three in a waltz for example.
The strong-weak, strong-weak-weak concept are part of how duple and triple meter work, and they form the basis for understanding compound and odd time.
4. Meter
A meter’s music theory definition is that it refers to the rhytmic organization of music into groups of pulses or beats. You will see this in a time signature at the beginning of music sheet.
A beat pattern, by definition, is an arrangement of beats and accents in a rhythm. These paterns are layered and to create grooves.
Different types of meters will evoke different moods and feelings for a song which is why this can have a significant impact on the overall sound.
Duple and Triple Meter
So far we’ve only discussed 3/4 and 4/4 time which are the two most common time signatures.
If you are interested in using compound time and odd time in your track, you need to understand how beats within any measure are felt in twos or threes.
It makes a bit more sense once you know how strong and weak beats in music work.
One way to visualize triple and duple meter is to imagine the difference between a rolling triangle and a rolling square with each new revolution being where the strong beat falls.
One way to visualize triple and duple meter is to imagine the difference between a rolling triangle and a rolling square
If you look at the strong and weak beats in a 4/4 bar, they can be separated into two groups of two duples– strong then weak, strong then weak.
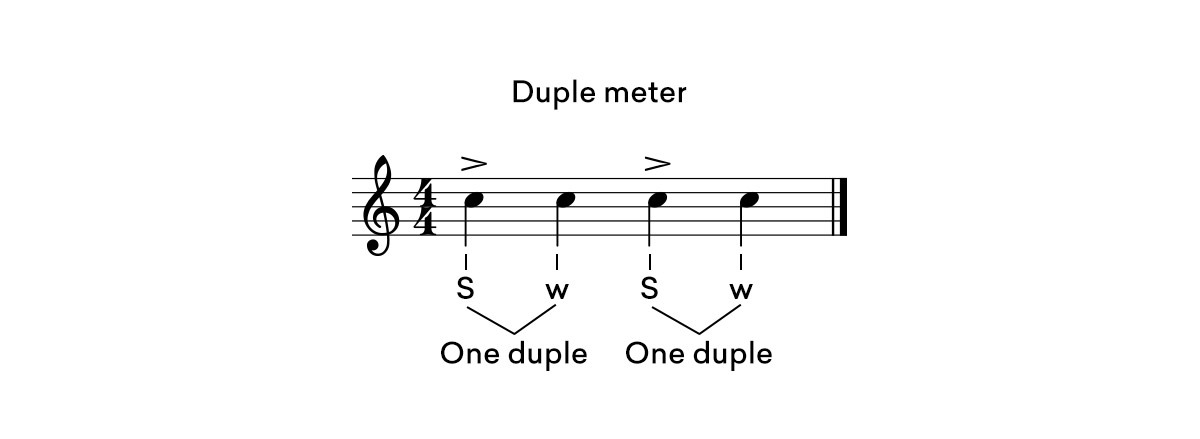
A strong-weak pattern signifies that duple meter is in play.
Since the bar is divided into two duples, 4/4 time is also sometimes referred to as quadruple time.
In a 3/4 bar, it’s just one triple group– strong, weak, weak.
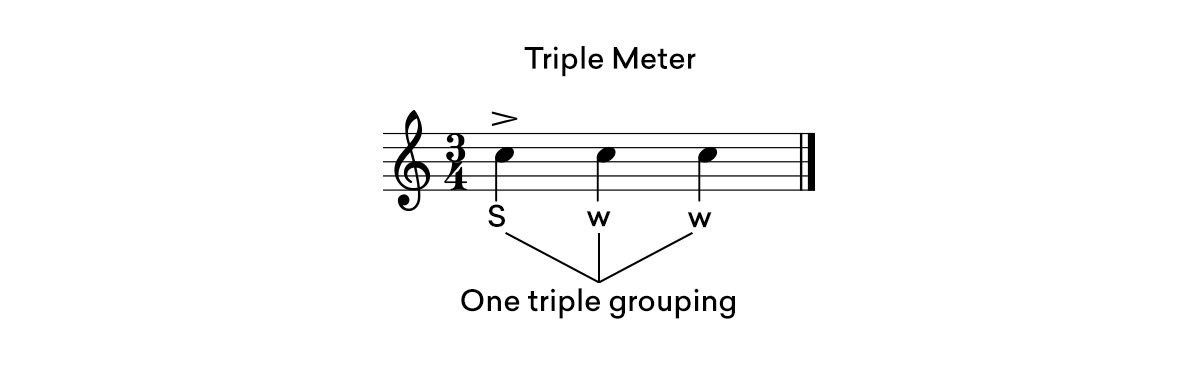
A strong-weak-weak pattern signifies that triple meter is in play.
Any rhythmic pattern or time signature can be divided into meters of two or three.
But meter isn’t the only way that beats are subdivided within a measure, simple and compound time adds another set of rules.
Simple vs. compound time
Simple and compound time are directly related to meter.
Meter defines how the rhythm is felt in terms of strong and weak beats.
Simple and compound time dictate whether a measures shorter notes (usually eighth notes) are divided into groups of either two or three.
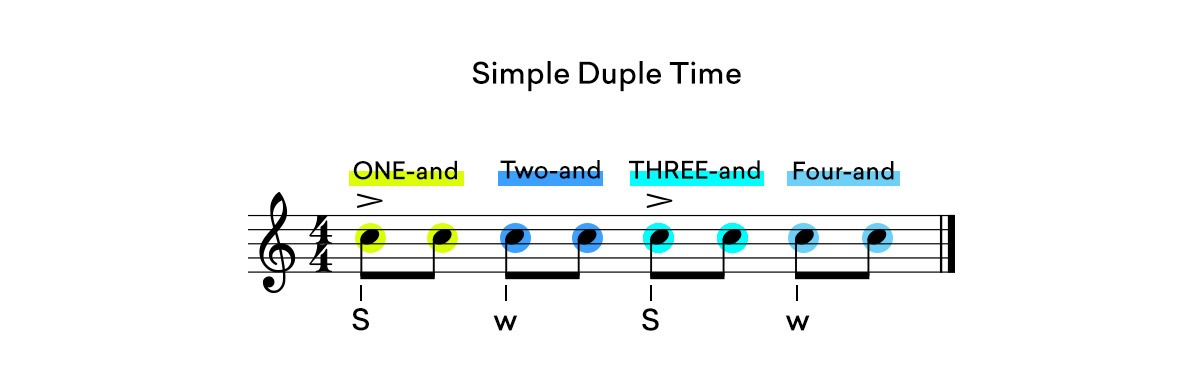
Simple time groups eighth notes into groups of two.
4/4 time is simple duple time. Its eight notes are counted ONE-and, two-and, THREE-and, four-and.
3/4 time is simple triple time. It is counted ONE-and, two-and, three-and.
Compound time groups eighth notes into groups of three.
6/8 and 9/8 are both examples of compound time.
In 6/8 compound duple time, notes are subdivided into two groups of three eighth notes.
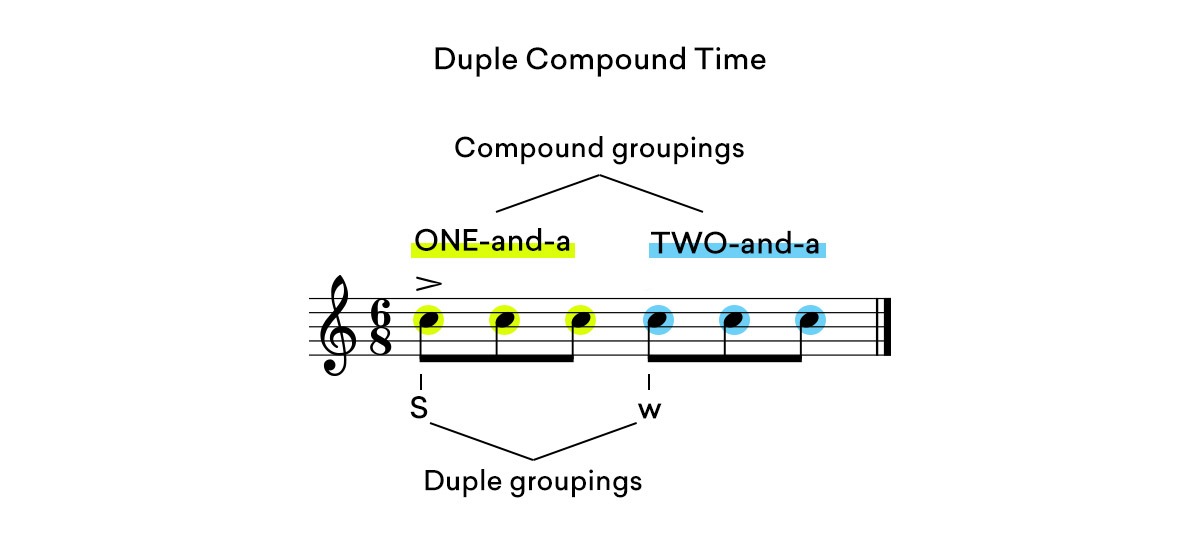
The eighth notes could be counted ONE-and-a, TWO-and-a.
Drake’s song Plastic Bag is a great example of a popular song that follows a 6/8 rhythm.
In 9/8 compound triple time notes are subdivided into three groups of three eighth notes.
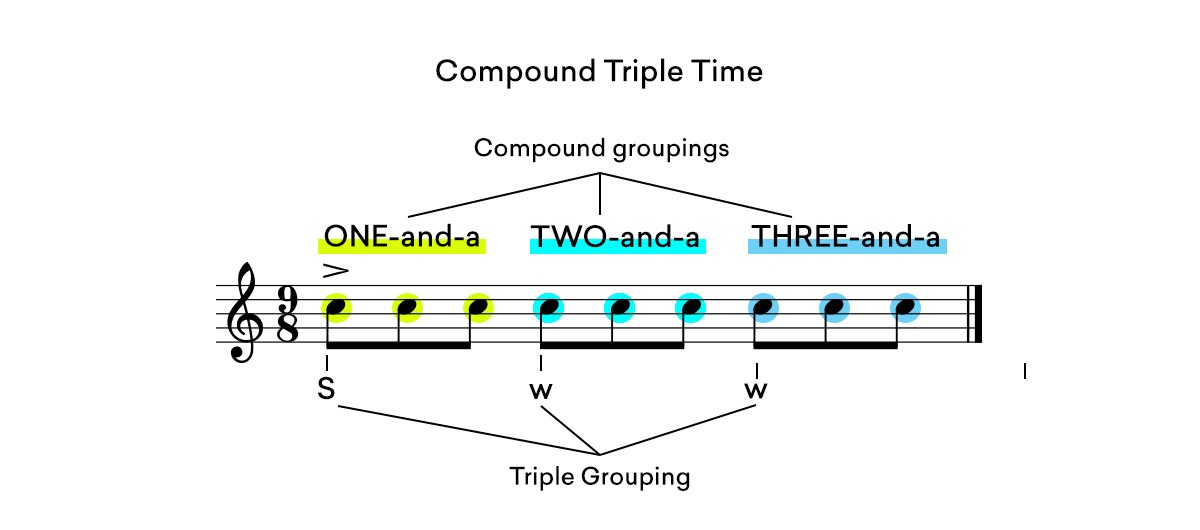
The eighth notes are counted ONE-and-a, TWO-and-a, THREE-and-a.
Dave Brubeck’s famous jazz track Blue Rondo A La Turk makes use of compound 9/8 time.
This track alternates between compound and odd 9/8 time, see if you can spot the difference!
Speaking of odd time…
Odd time
Odd time can be a little bit intimidating, there’s a lot to know.
But once you know how duple and triple meter works and feels you can easily handle any odd time pattern.
Odd time signatures take the rules behind simple and compound time and combine them.
That’s because any odd time signature follows a pattern based on some combination of duples and triples.
Odd time signatures follow a pattern based on some combination of duples and triples.
All you need to know is how each measure is subdivided into groups of two or three.
Consider the 5/8 time signature. It can be cut down to either a duple grouping followed by a triple grouping or a triple grouping followed by a duple grouping.
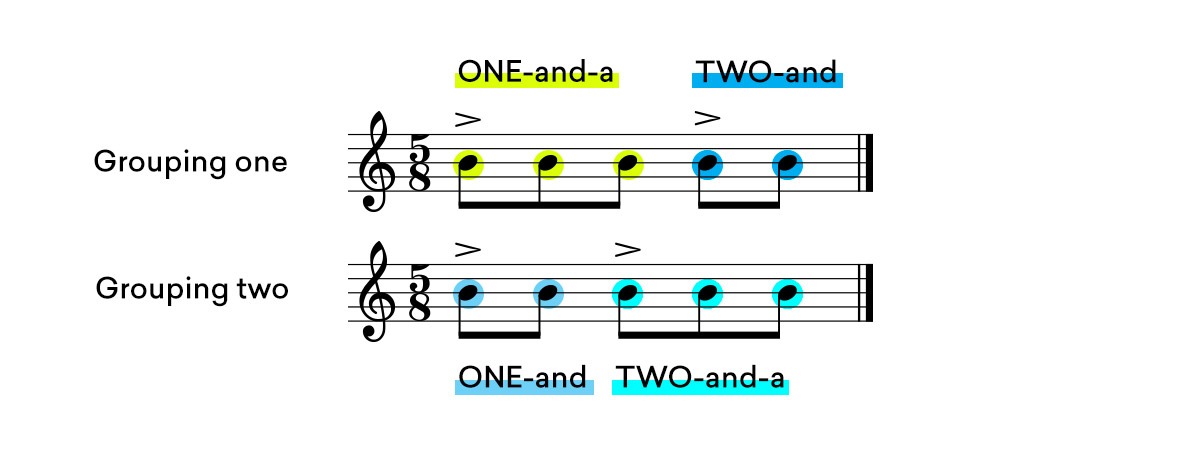
If it doesn’t make sense, try counting the time signature out loud but only in duples or triples.
So for a 5/8 time signature, you would either count it as ONE-and TWO-and-a or, ONE-and-a TWO-and.
So, looking at the Blue Rondo A La Turk example from above, the 9/8 section in odd time follows a ONE-and, TWO-and, THREE-and, FOUR-and-a format.
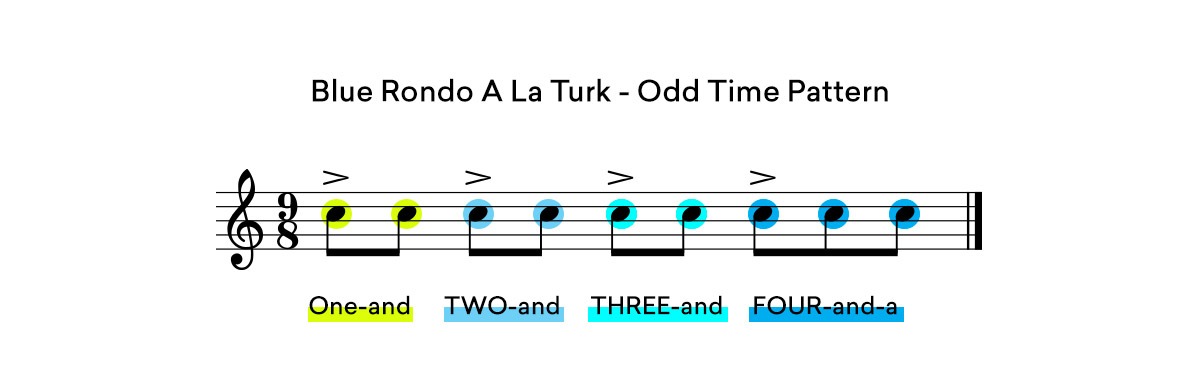
Once you know how duples and triple work in combination with one another you can easily count and feel the rhythm of any time signature.
5. Syncopation
Syncopation in rhythm is when notes are played off the main strong beat pulse of the time signature.
These syncopated rhythms occur either when a rhythm is played to emphasize a measure’s weak beats or off beats.
Syncopation on the weak beat usually creates a rhythmic structure that emphasizes the backbeat.
You hear this in a lot of music like Jazz and Disco where the two and four of a 4/4 bar are emphasized instead of the one and two.
Off beat syncopated rhythms emphasize the notes between the strong and weak beats.
Notes are played between the strong and weak beats in off beat syncopated rhythms.
But playing a quick note right before a strong beat can also emphasize the off beat, to create a syncopated feeling.
To play an off beat syncopated rhythm it always helps to count the off beats as you count through a bar of music.
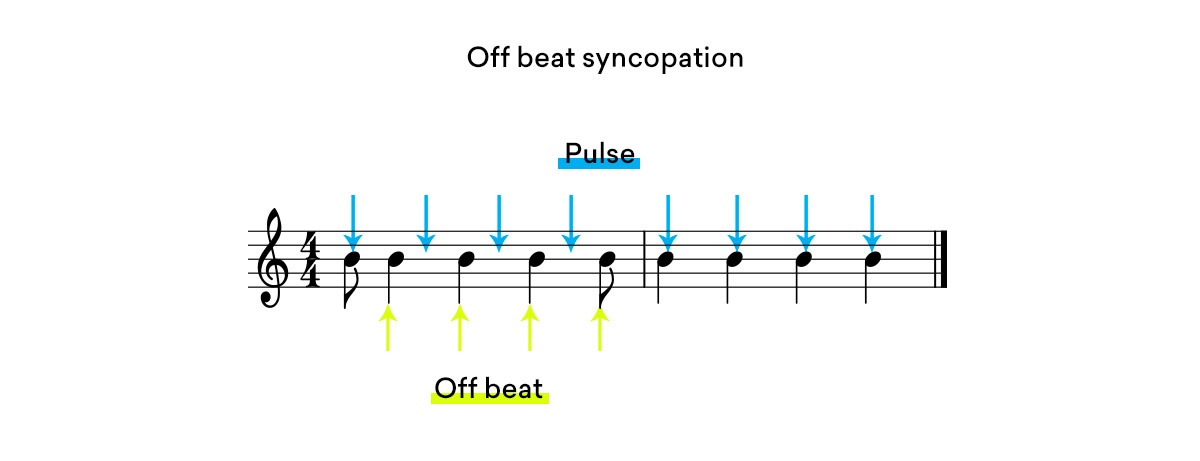
For example, in a 4/4 bar you would count it “one and two and three and four and”. The “ands” represent the space between the strong and weak beats.
6. Accents
Accents, in music, are the emphasis you will hear on a particular note or beat in a song. The idea is to make this part stand out. This is how musicians create dynamics in their music.
This can be achieved by playing a note more loudly, longer or by placing it in a more plrominent position in the song’s arrangement.
Accents are used to create interest within a piece of music or some variation. You might also hear it being used to create tension or release. When it comes to emoting through instrumentals, accents play a key role.
7. Tempo
Tempo is the speed and pace of how music is performed. If you’re tapping along to the beat in a song, then how fast you are tapping is the tempo of that song.
The tempo of a song measures beats per minute (BPM) so a song with 100 BPM would mean there are 100 beats being played in one minute.
Since tempo dictates the pace of music and how it is performed, it plays an important role in the flow of the rhythm. The tempo of a piece of music has a big imapct on the energy level and mood.
Faster, upbeat tempos are more exciting and high-energy. You’ll hear this in losts of dance music. Slower tempos are common in ballads.
Clap it out
It’s really good to have a theoretical understanding of rhythm because it can help you learn quickly.
But to develop great rhythmic sensibilities there’s nothing better than practicing.
If you are struggling to understand a particular rhythm, don’t be afraid to put your instrument down and clap it out.
You won’t get anywhere by practicing the wrong rhythm over and over again.
Rhythm more about togetherness and feeling the groove than it is about knowing how to read sheet music and notation. The rhythm’s definition in music has more to do with perception and feeling that it has to calculated placements of sound.
Jamming with others, listening to what they are playing and communicating with them through sound is an excellent and very fun way to develop your rhythmic sensibilities too.
Gear guides, tips, tutorials, inspiration and more—delivered weekly.
Keep up with the LANDR Blog.